
[ad_1]
A current research posted to the medRxiv* preprint server assessed the impression of prior extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination on the human immune response in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron an infection.
Numerous research have reported decrease susceptibility of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant in opposition to neutralizing antibodies. Subsequently, it’s essential to know the potential of earlier SARS-CoV-2 infections in modifying the human immune response in opposition to the novel Omicron variant.
 Examine: Prior vaccination allows a extra strong immune response to Omicron an infection. Picture Credit score: Christoph Burgstedt / Shutterstock
Examine: Prior vaccination allows a extra strong immune response to Omicron an infection. Picture Credit score: Christoph Burgstedt / Shutterstock
In regards to the research
Within the current research, researchers in contrast the antibody responses and the modifications in immune-transcriptome following SARS-CoV-2 Omicron an infection in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations experiencing gentle to reasonable coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) signs.
A complete of 57 Omicron-infected sufferers participated within the research, together with 34 people with no historical past of earlier COVID-19 vaccination and 23 people who had been vaccinated with two to 3 doses of the Pfizer BioNTech (BNT162b2) vaccine. Written and knowledgeable consent of those contributors was obtained. Recruitment and blood pattern assortment had been carried out between December 2021 and March 2022.
The workforce measured the binding immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody finish titers in opposition to a number of SARS-CoV-2-derived antigens through the mesoscale discovery (MSD) platform. Moreover, the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S), nucleocapsid (N) in addition to SARS-CoV-2 Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron variant S subdomains had been assayed utilizing serological samples collected from the contributors. The workforce additionally detected certain antibodies within the samples utilizing anti-human IgG antibodies.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binding inhibition was assessed utilizing an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to quantify the antibodies that inhibit the binding of ACE2 to the subdomains of SARS-CoV-2 variant spike proteins. The workforce additionally carried out the extraction and purification of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and evaluated its focus and high quality.
The authors explored the immune transcriptome to look at the impression of prior COVID-19 vaccination on the immune response of the genome in direction of Omicron an infection. This was achieved by evaluating the impression of vaccines within the reference inhabitants which had no reported historical past of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination or an infection to that of sufferers beforehand contaminated with the Alpha variant.
The workforce in contrast the Omicron transcriptomes of the unvaccinated and vaccinated cohorts to that of a management cohort, consisting of 30 wholesome people belonging to the identical geographic area. Messenger ribonucleic acid [ sequencing (mRNA-seq)] was additionally carried out by purifying the poly-A-containing mRNA through poly-T oligo-hybridization.
Serological samples obtained from the Omicron-infected sufferers inside two days and after 13 days of analysis had been used for the measurement of circulating antibody responses and for the evaluation of neutralizing capability in opposition to the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type and Omicron spike proteins. The workforce additionally analyzed the activation of gene expression within the unvaccinated Omicron-infected sufferers as in comparison with that within the vaccinated sufferers.
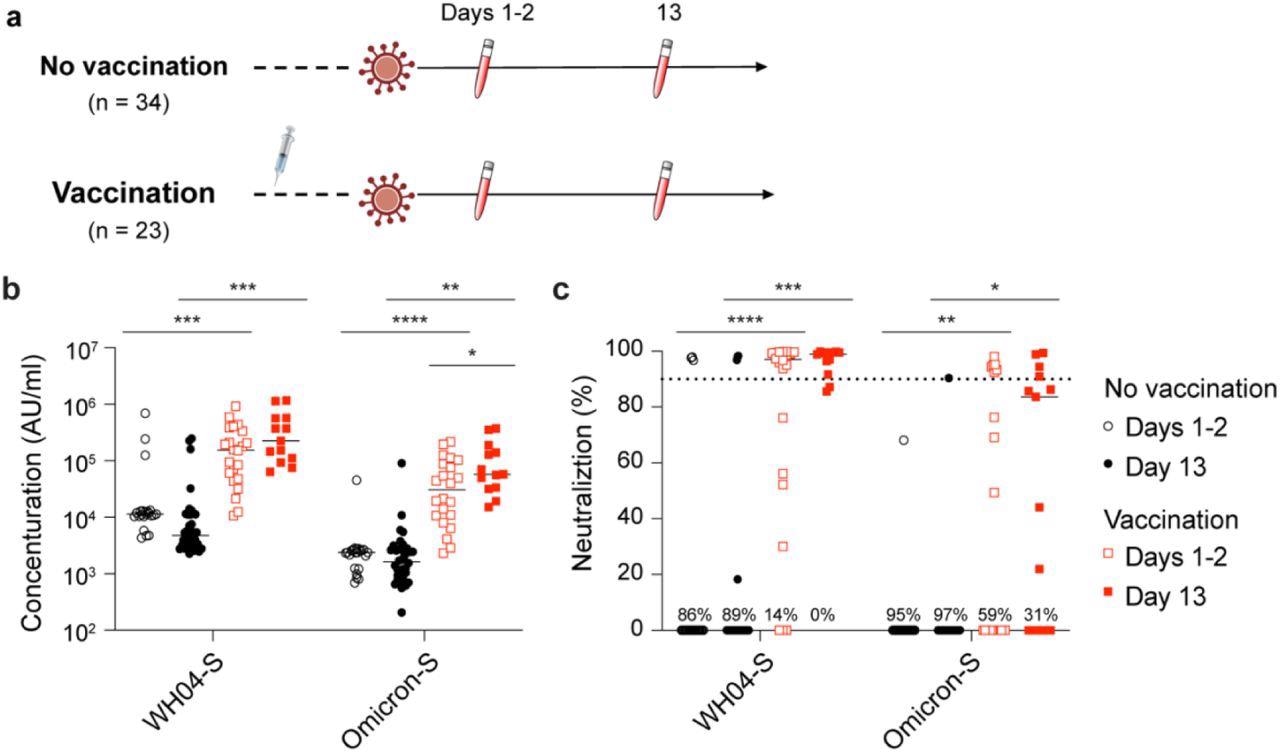
Examine design and antibody evaluation. a, Schematic presentation of the experimental workflow. All 57 research topics had been contaminated by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Of them, 23 had acquired two or three doses of the BNT162b2 vaccines and 34 had been unvaccinated (Desk S1). Blood was collected from research contributors at two timepoints after testing PCR optimistic. b, Plasma IgG antibody binding the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (spike) from the ancestral and Omicron strains within the unvaccinated and vaccinated Omicron sufferers. c, Neutralizing antibody response to virus spike protein of the ancestral and Omicron variants. p-value between two teams is from one-tailed Wilcoxon rank t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0, ****P < 0.0001. Line at median.
Outcomes
The research outcomes confirmed that one to 2 days after analysis of an infection, the degrees of anti-spike IgG had been the bottom in sufferers contaminated with the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type pressure and Omicron variant with no historical past of vaccination or an infection. The anti-S IgG ranges had been a minimum of 10 occasions larger in sufferers who had been beforehand vaccinated. A considerable enhance within the ranges of the anti-Omicron S antibodies was discovered within the vaccinated group inside 13 days of Omicron an infection whereas the anti-wild-type S ranges confirmed no such enhance. Furthermore, antibody ranges in opposition to any SARS-CoV-2 pressure confirmed no enchancment within the naïve group 13 days after the analysis of an infection.
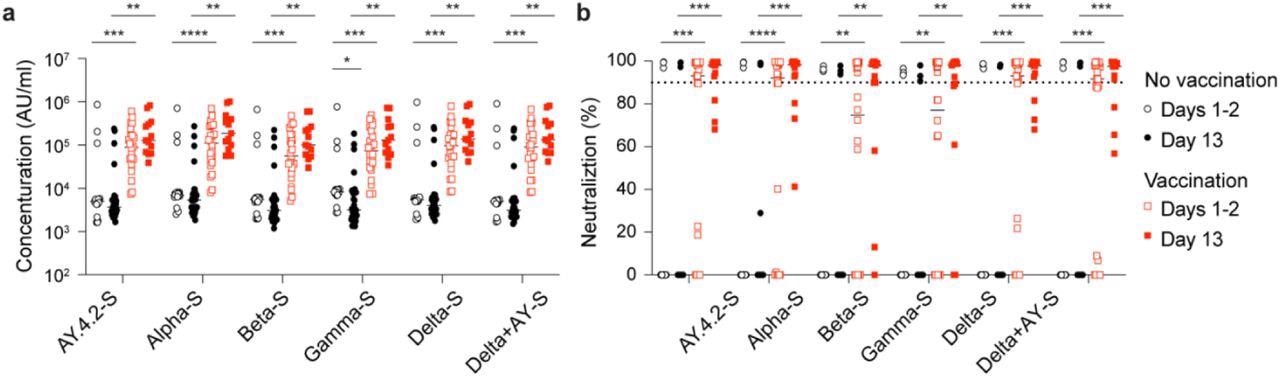
Antibody response of Omicron sufferers. a, Plasma IgG antibody binding the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (spike) from completely different strains within the no vaccinated and vaccinated Omicron sufferers. b, Neutralizing antibody response to virus spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variants. p-value between two teams is from one-tailed Wilcoxon rank t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0, ****P < 0.0001. Line at median.
The workforce discovered a noteworthy enhance within the neutralizing exercise in opposition to Omicron, significantly within the vaccinated cohort. Equally, a rise in anti-spike ranges was noticed in opposition to different SARS-CoV-2 variants. Moreover, a major induction of 489 and 732 gene expression was discovered within the naïve and the vaccinated group, respectively, whereas the genetic expression of 146 and 246 genes was correspondingly decreased. Notably, a rise in gene expression was noticed within the unvaccinated Omicron-infected inhabitants, which was additional discovered to be elevated within the Alpha-infected sufferers.
Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) related the induction of gene expression with innate immune responses, together with cytokine signaling and interferon responses. Important enrichment of innate immune genes was noticed in Alpha-infected hospitalized sufferers.
Conclusion
The research findings confirmed {that a} marked transcriptional response was discovered within the unvaccinated people; nevertheless, this response was not sufficiently expressed as in comparison with the vaccinated people. The researchers imagine that prior COVID-19 vaccination remarkably modified the transcriptome expression in Omicron-infected sufferers with stronger antibody responses in opposition to the virus. Nevertheless, the variations between the cohorts had been quantitative quite than qualitative.
*Necessary discover
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.
Journal reference:
- Prior vaccination allows a extra strong immune response to Omicron an infection. Hye Kyung Lee, Ludwig Knabl, Mary Walter, Yuhai Dai, Ludwig Knabl Sr., Magdalena Füßl, Yasemin Caf, Claudia Jeller, Philipp Knabl, Martina Obermoser, Christof Baurecht, Norbert Kaiser, August Zabernigg, Gernot M. Wurdinger, Priscilla A. Furth, Lothar Hennighausen, medRxiv preprint 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.24.22272837, https://www.medrxiv.org/content material/10.1101/2022.03.24.22272837v1
[ad_2]



