
[ad_1]
In a latest examine posted to the bioRxiv*preprint server, researchers evaluated the serum proteomic signatures of lengthy coronavirus illness (COVID) sufferers.
Persistent, novel, or recurrent signs post-acute an infection by extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have been termed as lengthy COVID or the post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC). The etiology of PASC signs is unknown; nonetheless, the signs could also be on account of persistent irritation, unresolved mobile harm, or delayed SARS-CoV-2 clearance. The medical heterogeneity of PASC warrants additional analysis.
 Examine: Persistent serum protein signatures outline an inflammatory subset of lengthy COVID. Picture Credit score: Donkeyworx / Shutterstock
Examine: Persistent serum protein signatures outline an inflammatory subset of lengthy COVID. Picture Credit score: Donkeyworx / Shutterstock
In regards to the examine
Within the current examine, researchers carried out serum proteomic profiling of PASC sufferers to elucidate the drivers of PASC signs.
Serum samples of 55 PASC people had been analyzed utilizing the Olink Discover 1536 panel. The contributors had been categorized as ‘PASC,’ ‘recovered,’ or ‘uninfected’ based mostly on the presence or absence of signs 60 days publish polymerase chain response (PCR)-confirmed acute coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) analysis. Blood samples had been collected from the uninfected contributors as soon as they entered the examine They had been collected from the PASC sufferers and recovered contributors publish 60 days and as much as a most of 379 days post-symptom onset (PSO), the acute section of COVID-19.
Hierarchical clustering was used for locating clusters of contributors with equivalent serum proteome signatures regardless of the COVID-19 standing or signs. Canonical pathways of the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) had been used for the proteomic evaluation. Consequently, 85 pathways had been recognized that considerably discriminated between PASC and the opposite two teams. The pathways had been merged into 54 modules, of which the modules that considerably distinguished every cluster had been recognized based mostly on the single-sample gene set enrichment evaluation (ssGSEA) scores.
The contributors had been assigned medical exercise scores that accounted for the symptom period and its influence on performing day by day actions throughout acute COVID-19. Moreover, the proteins expressed by the contributors of every cluster had been assessed. As well as, the proteomic signatures had been in comparison with these of the INCOV examine contributors to judge the generalizability of the current examine findings.
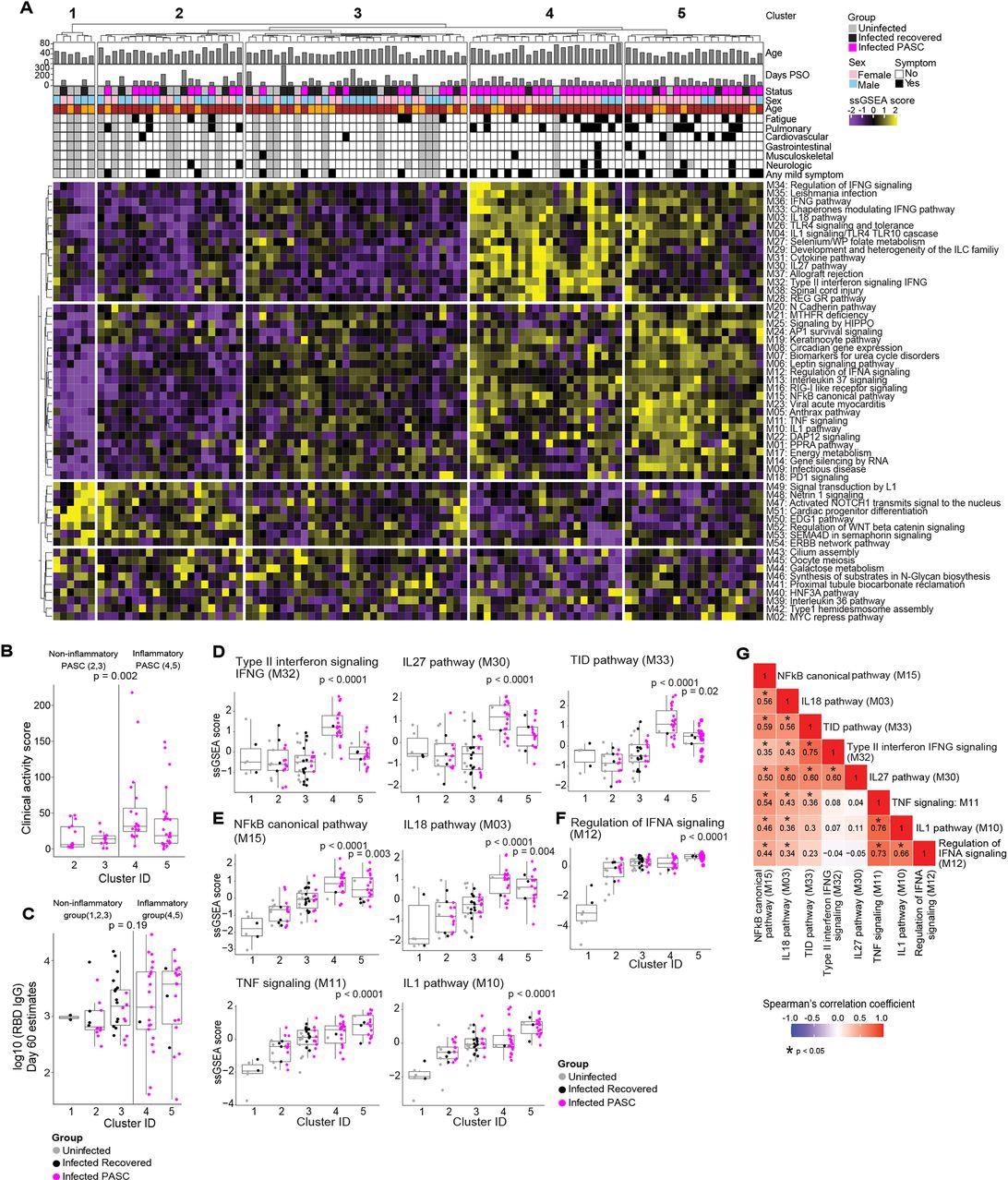
Serum proteomic clustering of PASC. (A) Heatmap of the rule-in methodology based mostly unsupervised clustering of Olink serum proteome information throughout all sufferers within the cohort (PASC + recovered + uninfected). Rows symbolize modules, columns symbolize samples and the scaled ssGSEA module rating throughout samples is depicted from low (purple) to excessive (yellow). The strategy identifies 2 clusters of topics with increased inflammatory module signatures (4 & 5) relative to the opposite three clusters of topics (1, 2, 3) that lack inflammatory signatures.
Outcomes
Within the hierarchical clustering evaluation, from the 54 modules, 5 distinct clusters had been recognized, of which clusters 1, 2, and three didn’t reveal inflammatory molecule enrichment (non-inflammatory clusters), whereas clusters 4 and 5 demonstrated remarkably enriched inflammatory molecules (inflammatory clusters).
The inflammatory clusters predominantly comprised PASC sufferers (91% and 80% in clusters 4 and 5, respectively), whereas the non-inflammatory clusters comprised solely recovered or uninfected contributors (cluster 1) or all of the three examine teams (clusters 2 and three, that comprised 48% and 28% PASC sufferers, respectively). The presence of PASC sufferers within the inflammatory and the non-inflammatory clusters is indicative of PASC heterogeneity.
The inflammatory clusters 4 and 5 had 234 and 296 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs), respectively. Within the inflammatory clusters, PASC sufferers demonstrated considerably elevated medical exercise scores in comparison with these within the non-inflammatory clusters. Nonetheless, there have been no important variations within the immunoglobulin G (IgG) titers towards the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding area (RBD) and the SARS-CoV-2-specific T lymphocyte responses among the many contaminated contributors (PASC sufferers and the recovered contributors) 60 days PSO amongst contributors within the 5 clusters.
Within the inflammatory clusters, enhanced enrichment of the NF-κB (nuclear issue kappa mild chain enhancer of activated B cells) pathways and their related chemokines and cytokines [interleukins (IL-1,18) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)] was noticed. Kind II interferons (IFN) [such as IFN-γ signaling proteins and IL-27] and IFN-α regulatory proteins had been extremely enriched notably in clusters 4 and 5, respectively.
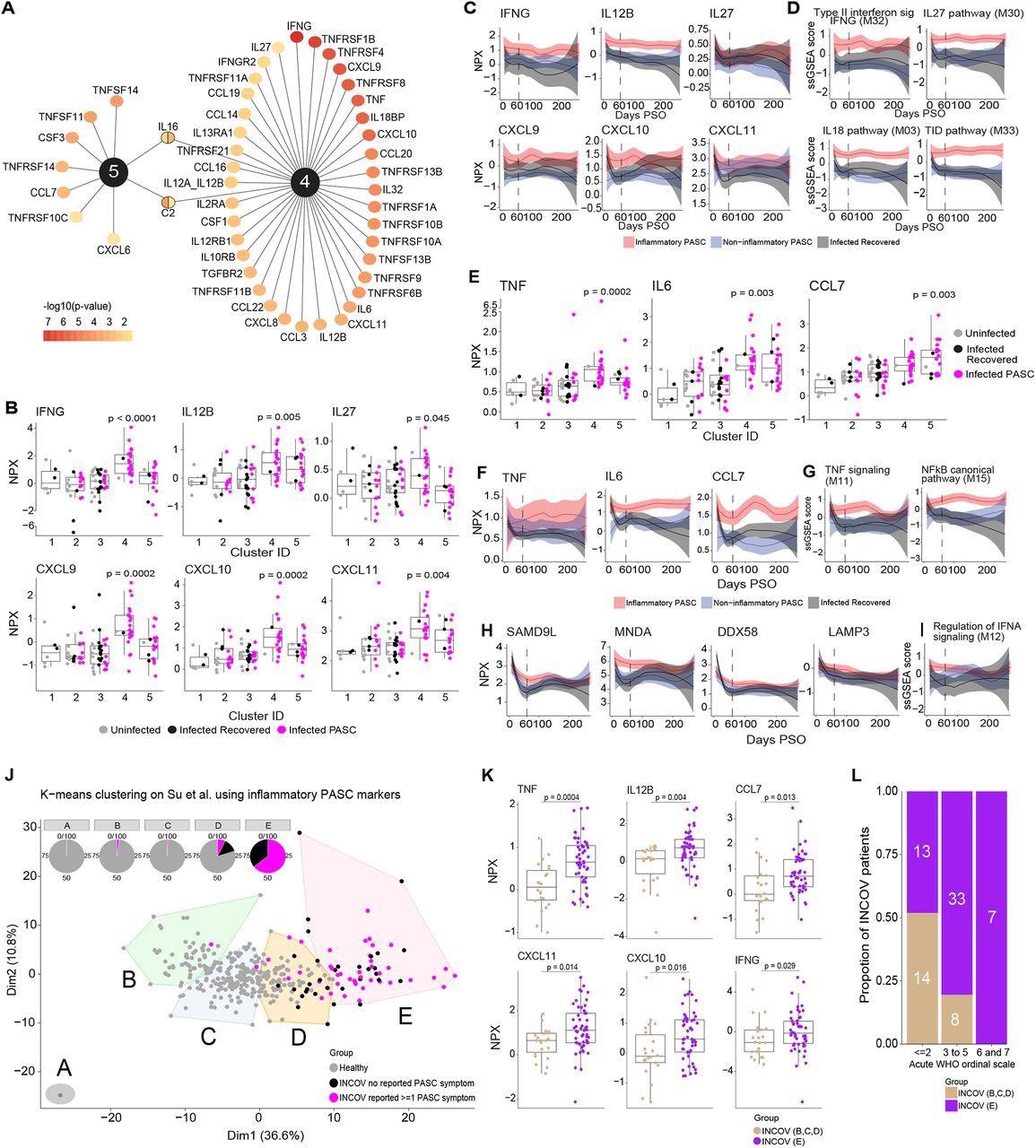
Key protein indicators driving inflammatory PASC signatures. (A) High ranked differentially expressed cytokines, chemokines, and cytokine/chemokine receptors by adjusted p-value of <0.05 which can be related to inflammatory protein clusters 4 & 5. The colour gradient of every node represents the -log10 adjusted p-value. (B) Field and jitter plots of olink Normalized Protein Expression (NPX) (y-axis) of IFN-γ and its associated cytokines and chemokines throughout clusters (x-axis) that had been considerably upregulated completely in cluster 4. P-values decided by Wilcoxon rank sum check had been calculated evaluating inflammatory cluster 4 and inflammatory cluster 5 independently to clusters 1,2,3. (C) Longitudinal loess match plots of Olink NPX of IFN-γ and its associated cytokines and chemokines on samples accessible from early acute an infection by means of >60 days PSO (x-axis). PASC sufferers from the inflammatory clusters 4 and 5 are represented right here as inflammatory PASC (purple), PASC sufferers from clusters 2 and three are represented right here as non-inflammatory PASC (blue) whereas the recovered sufferers are represented in black. (D) Longitudinal loess match plots of the ssGSEA scores (y-axis) of IFN-γ associated modules over time (x-axis). (E) Field and jitter plots of Olink NPX (y-axis) expression ranges of TNF, IL6 and CCL7 throughout clusters (x-axis) that had been considerably differentially upregulated clusters 4 and 5. P-values decided by Wilcoxon rank sum check had been calculated evaluating inflammatory cluster 4 and inflammatory cluster 5 independently to clusters 1,2,3. (F) Longitudinal loess match plots of Olink NPX (y-axis) of TNF, IL6 and CCL7 over time (x-axis). (G) Longitudinal loess match plots of the ssGSEA scores (y-axis) of TNF and NF-κB associated signaling modules over time (x-axis). (H, I) Longitudinal loess match plots of Olink NPX and ssGSEA scores (y-axes) of type-I IFN-driven proteins and the IFN-α module time beyond regulation (x-axis) respectively. (J) Okay-means unsupervised clustering of Olink proteomic information from Su Y et al (2022) exhibiting 5 clusters of INCOV sufferers and wholesome controls. Pie charts present the share of every cluster consisting of INCOV sufferers and wholesome topics. (Okay) Cytokines/chemokines considerably upregulated within the INCOV cluster E vs. INCOV from clusters B,C, and D. P-values had been decided by a Wilcoxon rank sum check. (L) Distribution of various illness severities (as judged by WHO ordinal scale) throughout INCOV sufferers in cluster E vs INCOV sufferers in clusters B,C,D. Y-axis and the numbers in bar graphs symbolize proportion and variety of sufferers per INCOV group in every WHO scale bin respectively.
A big correlation was noticed among the many module scores i.e., elevated IL-18,27 and NF-κB signaling protein ranges had been noticed in sufferers with elevated IFN-γ signaling protein ranges. Likewise, elevated IL-1, IFN-α, and NF-κB signaling molecule ranges had been noticed in sufferers with elevated TNF signaling protein ranges. Among the many immune pathways, the proteins related to NF-κB signaling [especially TNF-associated] and IFN kind II signaling confirmed the best enrichment. The prolonged evaluation confirmed that the degrees of IL-12, TNF, and kind I IFN, IFN-γ, and their related signaling molecules had been elevated amongst PASC inflammatory clusters all through the examine.
Over 160 proteins equivalent to IFN-γ, IL12, C-X-C motif ligands (CXCL-10,11), TNF, and C-C motif ligand 7 (CCL7), DExD/H-box helicase 58 (DDX58), and lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 3 (LAMP3) within the inflammatory clusters overlapped with cluster E of the INCOV examine. Of the 5 INCOV clusters, cluster E demonstrated important enrichment of 79% of the protein traits of inflammatory PASC and 64% of the cluster E sufferers had persistent PASC signs. Subsequently, cluster E of the INCOV examine was much like the inflammatory clusters 4 and 5 of the current examine. Moreover, INCOV cluster D comprised PASC, recovered, and wholesome people, much like cluster 2. The remaining clusters (A, B, and C) of the INCOV examine predominantly comprised wholesome controls.
Of curiosity, most INCOV sufferers of cluster E exhibited World Well being Group (WHO) ordinal rating ≥3 which mirrored the affiliation between COVID-19 severity and protracted irritation.
Examine findings revealed serum proteomic signatures of lengthy COVID sufferers and fascinating immune molecules that might be targets for growing anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies.
*Necessary discover
bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information medical apply/health-related habits, or handled as established data.
Journal reference:
- Persistent serum protein signatures outline an inflammatory subset of lengthy COVID. Aarthi Talla, Suhas V. Vasaikar, Gregory Lee Szeto, Maria P. Lemos2, Julie L. Czartoski, Hugh MacMillan, Zoe Moodie, Kristen W. Cohen, Lamar B. Fleming, Zachary Thomson, Lauren Okada, Lynne A. Becker, Ernest M. Coffey, Stephen C. De Rosa, Evan W. Newell, Peter J. Skene, Xiaojun Li, Thomas F. Bumol, M. Juliana McElrath, Troy R. Torgerson, bioRxiv preprint 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.09.491196, https://www.biorxiv.org/content material/10.1101/2022.05.09.491196v1
[ad_2]



